Choosing the right Membrane Dosing Pump is crucial for effective fluid control. The global market for membrane dosing pumps is projected to reach $2 billion by 2025, showing robust growth. According to industry expert John Smith, "Selecting the appropriate pump is vital for optimal performance in various applications."
Membrane dosing pumps are used in water treatment, agriculture, and chemical industries. These pumps ensure precise dosing, which impacts overall efficiency and product quality. A poor choice can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
Key factors include flow rate and chemical compatibility. Users often overlook the importance of proper sizing. Miscalculating these needs can result in system failures, impacting production timelines. Careful consideration and expert consultation can help in making the right choice.
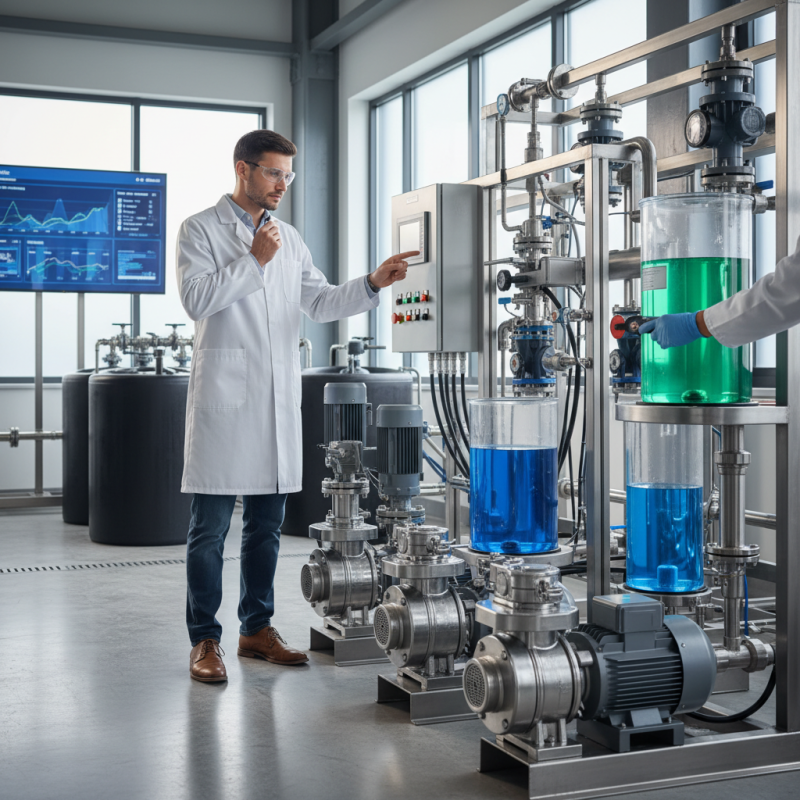

Membrane dosing pumps play a vital role in various industries. They are designed to handle precise fluid dosing. These pumps are especially useful in pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and food processing. Their ability to deliver consistent and accurate dosage makes them indispensable. Choosing the right pump starts with understanding how they work.
These pumps use a flexible membrane to create a vacuum, drawing in fluid. The membrane moves back and forth, displacing the fluid through a discharge port. This process ensures minimal pulsation, which is crucial for accurate dosing. Users must consider factors like flow rate and pressure. The application type may require different specifications.
Not every pump will suit your needs perfectly. There may be trial and error in finding the right fit. Awareness of the application requirements can avoid wasted time and resources. Pay attention to features like material compatibility. These details impact performance and longevity. Challenges arise when the pump cannot handle corrosive substances. It’s essential to reflect on these aspects to ensure optimal operation.
When selecting a membrane dosing pump, several key factors come into play. Flow rate is a primary consideration. Most applications demand a specific output. Understanding the required flow rate helps narrow down choices. For example, a report by the International Society for Automation states that accurate dosing can reduce chemical waste by up to 30%. This illustrates the importance of flow precision.
Another crucial aspect is the materials used in construction. The pump materials must be compatible with the chemicals involved. For aggressive chemicals, corrosion-resistant materials are crucial. A mismatch can lead to equipment failure or safety hazards. Consider the potential costs of maintenance and replacement. These expenses can exceed initial savings from cheaper alternatives.
Tips: Always assess the chemical properties. Consult technical data sheets. Ensure the pump meets your specific application needs.
The drive for energy efficiency is also significant. Today’s market demands pumps that consume less power while maintaining performance. Data indicates that energy-efficient dosing pumps can reduce operational costs by 15-20%. However, achieving this may require a higher upfront investment. Reflecting on the total lifecycle cost is essential. Balancing initial costs and long-term savings is often challenging but vital.
When selecting a membrane dosing pump, understanding the differences in types is crucial. Diafragm pumps generally handle lower flows but offer high accuracy. According to a recent industry report, diaphragm pumps provide
±1% accuracy, making them suitable for chemical processing. They are reliable but can wear out with aggressive fluids. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure continued precision.
Peristaltic pumps are another option. They are more flexible and can handle a wider range of fluids. With a flow rate that can exceed
100 liters per hour, they are advantageous for larger operations. However, the accuracy varies, typically around
±2% to ±5%, based on the application and conditions. They require frequent tube replacements, which can lead to increased operational costs.
Moreover, solenoid-driven pumps are known for their compact design. They are easy to install and operate under varying conditions. However, they usually offer lower flow rates, capped around
10 liters per hour. Their lifespan can be shorter due to mechanical wear. Users should keep this in mind, as the
initial cost savings may lead to higher maintenance expenses down the line. These factors are critical when considering the best fit for your specific needs.
When selecting a membrane dosing pump, maintenance and operational efficiency are key factors. Regular checks of the pump's seals and connections are essential. Ensuring there are no leaks is vital for proper operation. A small leak can lead to significant issues over time. It's also important to clean the pump regularly. This prevents clogging and maintains flow rates.
Consider the frequency of use. If the pump operates continuously, scheduled maintenance becomes even more necessary. Check the diaphragm for wear and tear often. Over time, wear can affect accuracy. Keeping detailed records of maintenance can help identify patterns or recurring issues.
Evaluate the environment in which the pump operates. Harsh conditions may lead to more frequent repairs. Dust, moisture, or corrosive materials can impact durability. Sometimes, investing in a more robust model pays off. Reflecting on the pump's performance over time helps in making informed decisions. Familiarity with operational limits is crucial for long-term efficiency.
This bar chart illustrates different specifications of three membrane dosing pumps, focusing on key parameters such as flow rate, maximum pressure, power consumption, accuracy, and maintenance frequency. This data can help in making informed decisions when choosing the right dosing pump for specific needs.
Choosing the right membrane dosing pump can greatly impact your operations. A cost-benefit evaluation is crucial. Look closely at upfront costs. A cheaper pump may save money initially. However, consider long-term reliability. Will it require frequent repairs? Maintenance costs can pile up.
Evaluate efficiency as well. Higher efficiency can lead to lower operational costs. Make a list of your specific needs. The right pump must meet both your budget and your requirements. For instance, how much liquid will you pump daily?
Don’t overlook energy consumption. Some pumps can consume much power. You might end up spending more than expected. Reflect on your choices carefully. Each detail counts when making a decision. A decision that may look perfect now might pose challenges later. Remember, the right fit today may not be the best tomorrow.
| Pump Type | Flow Rate (L/h) | Pressure (bar) | Power Consumption (W) | Estimated Cost ($) | Maintenance Cost/Year ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm Pump | 100 | 3 | 50 | 400 | 50 |
| Peristaltic Pump | 150 | 2 | 65 | 500 | 30 |
| Solenoid Pump | 50 | 4 | 40 | 300 | 25 |
| Gear Pump | 200 | 5 | 75 | 600 | 40 |






