Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) is an innovative and effective method widely used in water treatment processes to separate suspended solids from liquids. This technology leverages the principles of buoyancy and surface tension to enhance the clarification of wastewater, making it a critical component in various industries, including food processing, petrochemical, and municipal wastewater treatment. By creating micro-bubbles that adhere to particles, DAF enables these solids to float to the surface, where they can be easily removed and treated.

As environmental concerns grow and regulatory standards become more stringent, the demand for efficient and sustainable water treatment solutions is more pressing than ever. Dispersed Air Flotation stands out as a versatile technique that not only improves water quality but also reduces the footprint of treatment plants. Understanding how DAF operates and its benefits is essential for industries seeking to optimize their wastewater management systems. This article delves into the mechanics of DAF and explores its applications, advantages, and the role it plays in safeguarding our water resources.
Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that utilizes microscopic air bubbles to separate contaminants from water. In this method, air is dissolved in the water under high pressure and then released at atmospheric pressure, resulting in the formation of numerous tiny bubbles. These bubbles adhere to suspended particles, making them buoyant and causing them to rise to the surface. This efficient separation mechanism allows solids, oils, and other impurities to be skimmed off, leading to cleaner water.
The process of DAF is particularly advantageous in treating industrial wastewater and municipal sewage, where conventional methods may fall short. By enhancing the removal of suspended solids and colloidal materials, DAF systems can significantly improve water quality. Factors such as bubble size, contact time, and flow rate play crucial roles in the effectiveness of the treatment. Overall, DAF represents a crucial innovation in water treatment technology, providing an efficient solution for achieving high levels of water purity.
This bar chart illustrates the performance metrics of a Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) system in water treatment. Key metrics include the removal efficiency, energy consumption, and chemical dosage used for treating water, providing insights into the operational efficiency of DAF technology.
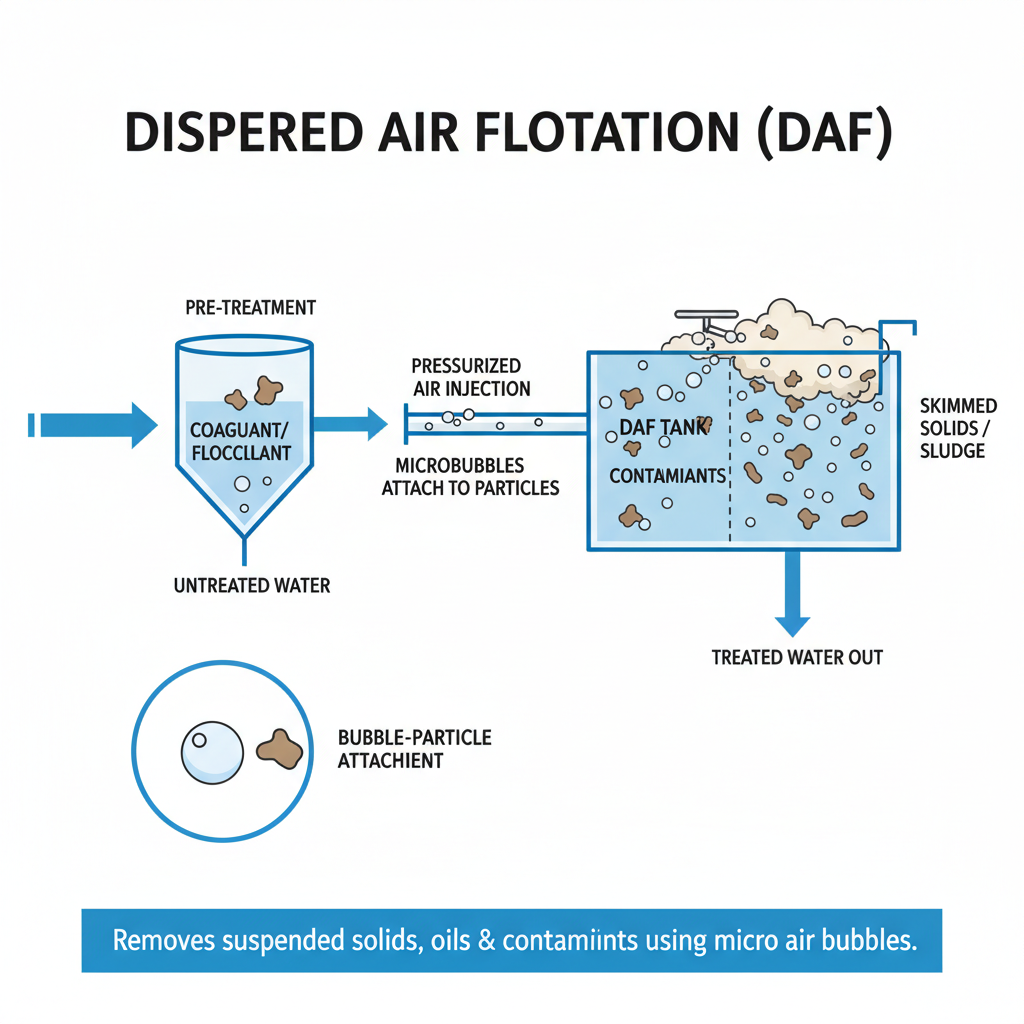
Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) is an innovative water treatment process that effectively removes suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants from water. The principle of operation hinges on the introduction of tiny air bubbles into the water, which adhere to the particulate matter, causing it to rise to the surface. In a typical DAF system, water is pre-treated to enhance separation, followed by aeration where air is injected under pressure. When this pressure is released, microbubbles form, which then attach themselves to the impurities within the water.
As the bubbles rise, they create a buoyant effect, lifting the flocculated solids to the surface, where they form a froth layer. This froth can then be easily skimmed off, leaving behind treated water that is significantly clearer and cleaner. The effectiveness of DAF lies in its ability to operate efficiently over a wide range of influent conditions, making it suitable for various applications, from municipal wastewater treatment to industrial processes. The design and operation of the DAF system can be tailored to meet specific treatment needs, enhancing its versatility and efficiency in water treatment.
Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) is a crucial technology in water treatment, effectively removing suspended solids and oils from wastewater. The key components of a DAF system work together to facilitate this process, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. The primary elements include the flotation chamber, air pressure system, and the collection mechanism. The flotation chamber serves as the central area where air and treated water interact, while the air pressure system generates microbubbles that attach to contaminants, causing them to rise to the surface for removal. The collection mechanism then gathers these floating materials for further processing.
When setting up a DAF system, keep in mind that proper maintenance of the air pressure system is essential. Regularly checking for leaks and ensuring that the air compressor operates efficiently can significantly enhance the system’s performance. Additionally, continuously monitoring the water quality entering the flotation chamber can help in adjusting the chemical dosing if required for optimal coagulation.
The material used in the construction of the flotation chamber is another critical aspect to consider. Selecting corrosion-resistant materials can extend the lifespan of the system and minimize operational disruptions. By paying attention to these key components and tips, a DAF system can be a powerful tool in effective water treatment processes.
| Component | Function | Material | Typical Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved Air System | Generates microbubbles for flotation | Stainless Steel | Varies |
| Flotation Cell | Where separation occurs | Fiberglass | 10-15 ft length |
| Clarifier | Removes floatation sludge | Concrete | Varies |
| Pump | Circulates water | Cast Iron | 5-10 hp |
| Air Compressor | Supplies compressed air | Aluminum/Steel | 5-50 hp |

Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) is an effective water treatment technology utilized across various industries. One of the primary applications of DAF is in municipal wastewater treatment, where it assists in the removal of suspended solids and fats, oils, and greases. By introducing fine air bubbles into the wastewater, these bubbles attach to the particles, making them buoyant and facilitating their rise to the surface, where they can be collected and removed. This process significantly enhances the efficiency of primary clarification and reduces the burden on secondary treatment systems.
In industrial settings, DAF finds applications in processing plants, particularly in food and beverage industries, where high levels of organic matter and fats are common. The flotation process helps in pre-treating wastewater before it enters biological treatment units, thereby improving overall treatment effectiveness and operational efficiency. Additionally, DAF is increasingly used in oil and gas operations for the treatment of produced water, contributing to environmental protection by ensuring that harmful elements are effectively separated before discharge. Its versatility and effectiveness make DAF a preferred choice in diverse water treatment scenarios.
Dispersed Air Flotation (DAF) technology is increasingly adopted in water treatment processes due to its distinct advantages. One of the primary benefits is its ability to effectively separate suspended solids and oils from water, achieving removal efficiencies of up to 98% under optimal conditions. This technology harnesses tiny air bubbles that adhere to contaminants, allowing them to rise to the surface for easier removal. As water scarcity issues become more pressing, the DAF system emerges as a sustainable solution, particularly in industries where wastewater management is critical.
However, DAF technology also presents some limitations. The initial capital investment can be substantial, which may deter smaller facilities from implementing such systems. Moreover, DAF units require careful monitoring and maintenance to function optimally. Factors such as water chemistry and temperature play significant roles in the performance of the system. According to a report by the American Water Works Association, understanding these variables is essential for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of DAF installations.
Tip: Regularly assess the water quality and adjust the DAF operations accordingly to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, conducting routine maintenance checks can help mitigate potential downtime and ensure consistent treatment results.






