Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) has emerged as a pivotal technology in the realm of water treatment, renowned for its ability to efficiently remove suspended solids and improve water clarity. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in the field of water treatment and DAF systems, "The key to effective water treatment lies in the innovative use of Dissolved Air technology, which significantly enhances the separation and removal processes." This powerful technique harnesses the principles of buoyancy and air dissolution, making it an invaluable solution for various industries facing water quality challenges.
In today’s world, where water pollution poses significant environmental and health risks, adopting advanced treatment methods like DAF is crucial. The process not only eliminates contaminants but also paves the way for sustainable water management practices, ensuring a more secure water future. Understanding how to leverage Dissolved Air technology can empower industries to achieve compliance with strict environmental regulations while promoting responsible water usage. This article delves into the operational mechanisms of DAF, its applications, and best practices for implementation, illustrating how it stands to revolutionize water treatment solutions across sectors.

Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is an effective water treatment process that utilizes the principles of buoyancy and air dissolution to remove contaminants from water. The basic principle involves dissolving air in water under pressure and then releasing it into a flotation tank. As the pressure drops, the dissolved air forms tiny bubbles that attach to suspended particles, causing them to rise to the surface. This creates a froth layer that can be easily skimmed off, leaving behind clearer water. This method is particularly useful for treating industrial wastewater, removing oils, fats, and suspended solids efficiently.
When implementing DAF systems, here are a few tips to enhance performance. First, ensure proper sizing of the DAF unit based on the expected flow rate and contaminant load; this will optimize efficiency and prevent overloading. Second, maintain appropriate chemical dosing for coagulants and flocculants, as they help improve the aggregation of particles, making them easier to remove. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the flotation system are also crucial to ensure that it operates at peak efficiency and to extend its service life.
Additionally, understanding the influent characteristics can significantly impact the DAF process. Conducting thorough water quality assessments prior to treatment allows for tailored adjustments to the system, further improving its effectiveness. This proactive approach influences not just the operational parameters but also the overall quality of the treated effluent, ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
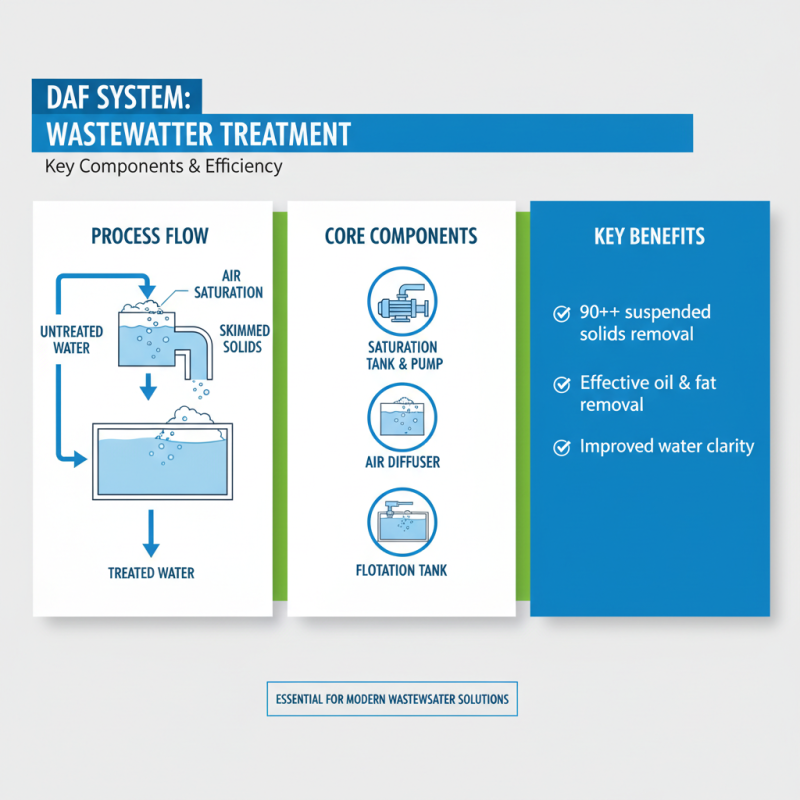
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) systems are increasingly recognized as an essential technology in wastewater treatment, providing highly effective solutions for the removal of suspended solids, oils, and fats. The key components of DAF systems play a critical role in their efficiency and overall performance. At the core of these systems is the flotation tank, designed for optimal hydraulic flow and retention time, allowing for the effective separation of solids from the water. According to industry reports, a well-designed DAF system can achieve a removal efficiency of 90% or more for suspended solids, making it a pivotal choice for various applications.
Another crucial component of DAF systems is the air dissolution mechanism. This typically involves the use of high-pressure pumps to saturate water with air, creating microscopic bubbles that adhere to solid particles during the flotation process. The size and distribution of these bubbles are vital for maximizing flotation efficiency. Research indicates that maintaining a bubble size of 20-50 microns can significantly enhance the separation process. Furthermore, the introduction of chemicals to coagulate andflocculate particles aids in forming larger aggregates that rise to the surface, thereby streamlining the overall treatment process.
Finally, the sludge removal and skimming systems are instrumental in maintaining operational efficiency. Effective removal of floatable sludge not only prevents system clogging but also enhances the quality of treated water. As per data from treatment facilities, neglecting this component can lead to a substantial decrease in treatment efficiency, underscoring the importance of proper maintenance and design in DAF applications. These elements combined provide a comprehensive framework for utilizing DAF technology effectively in various water treatment scenarios.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is an essential technique employed in diverse water treatment applications, effectively removing suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants. The implementation of DAF systems follows a systematic approach that encompasses several critical steps. Initially, the process begins with the pre-treatment phase, where inflow water undergoes screening to eliminate large debris and particulate matter. According to the Water Environment Federation, about 80% of total suspended solids can be efficiently removed during this stage, enhancing the performance of subsequent treatment processes.
Following pre-treatment, the next step involves saturating water with air under pressure. When this pressurized water is released, microbubbles form and attach to suspended particles. This agglomeration causes the particles to rise to the surface, creating a sludge layer that can be easily scraped off. Research indicates that the efficiency of this flotation process can reach up to 99% in terms of solid removal rates, especially in treating industrial wastewater. Finally, the collected sludge is either disposed of or further processed, while the clarified water continues to undergo additional treatments as necessary.
In aggregating these steps, DAF not only streamlines water treatment processes but also offers a sustainable solution that aligns with modern environmental standards.
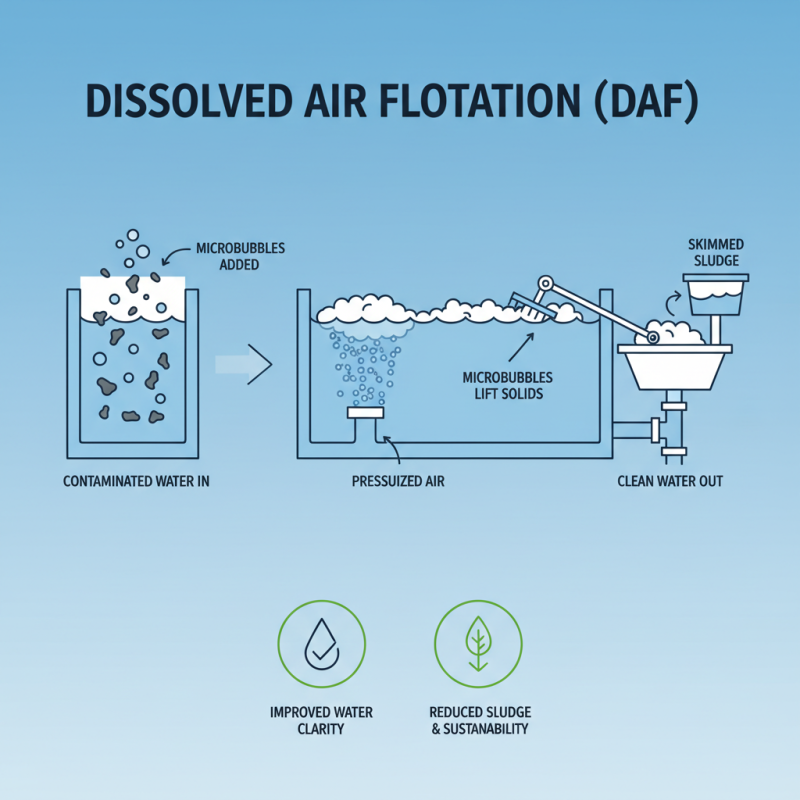
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is an innovative technology widely used in water treatment processes to improve water quality. One of the key benefits of DAF is its ability to effectively remove suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants, making it a preferred choice for various applications. Its efficiency lies in the creation of micro-bubbles that attach to the contaminants, causing them to rise to the surface for easy removal. This method not only enhances the clarity of water but also reduces sludge production, leading to a more sustainable operation.
When considering the application of DAF systems, industries such as food processing, wastewater treatment, and petrochemical operations have found significant advantages. Utilizing DAF helps in meeting regulatory compliance and improving overall environmental impact. Moreover, the technology is adaptable and can meet varying flow rates, which makes it suitable for both large and small-scale operations.
**Tips:** When implementing a DAF system, it is crucial to monitor the chemical dosing accurately to maintain optimum performance. Additionally, routine maintenance ensures that the system operates efficiently and prolongs its lifespan. Investing in proper training for staff will also enhance the operation and troubleshooting capabilities, leading to better outcomes in water treatment processes.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) technology presents an effective method for treating wastewater, yet its application is not without challenges. One common obstacle is the variation in influent characteristics, which can significantly impact the performance of DAF systems. According to a study by the Water Environment Federation, fluctuations in solids concentration can lead to inconsistent separation efficiency. Addressing this issue often requires operators to adjust operational parameters such as air saturation and retention time to adapt to varying influent conditions, ensuring optimal performance across different scenarios.
Another frequent challenge faced by DAF systems is the potential for fouling on the flotation equipment, which can hinder performance and lead to increased maintenance costs. Research indicates that the accumulation of grease, oils, and other organics can diminish the effective flotation process. To combat this, regular monitoring and maintenance schedules are essential. Implementing pretreatment measures, such as screening and sedimentation, can further reduce the load on the DAF system and enhance its overall efficiency. Furthermore, leveraging advanced monitoring technologies can provide real-time data, allowing for timely adjustments to maintain optimal operation and reduce downtime.






