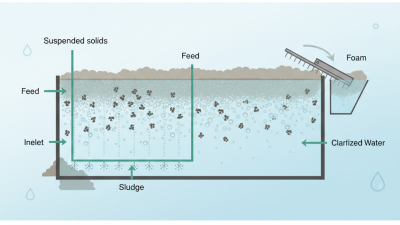
A Dissolved Air Flotation System (DAF) is an effective method for water treatment. It primarily focuses on removing suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants. The technology relies on the creation of tiny air bubbles that adhere to particles. This process allows the particles to float to the surface, forming a scum layer. The scum is then removed, leaving cleaner water.
In practice, DAF systems serve various industries, including food processing and wastewater management. The design can vary based on specific needs. While the process is efficient, it does come with challenges. For instance, the system requires careful monitoring. Any fluctuation in the input water quality can affect performance. Additionally, not all pollutants are effectively removed, prompting further treatment.
In summary, understanding how a Dissolved Air Flotation System operates is crucial for those in water treatment fields. Its advantages are notable, yet continuous evaluation of its effectiveness is essential. The balance between efficiency and limitations makes it a topic worth exploring further.
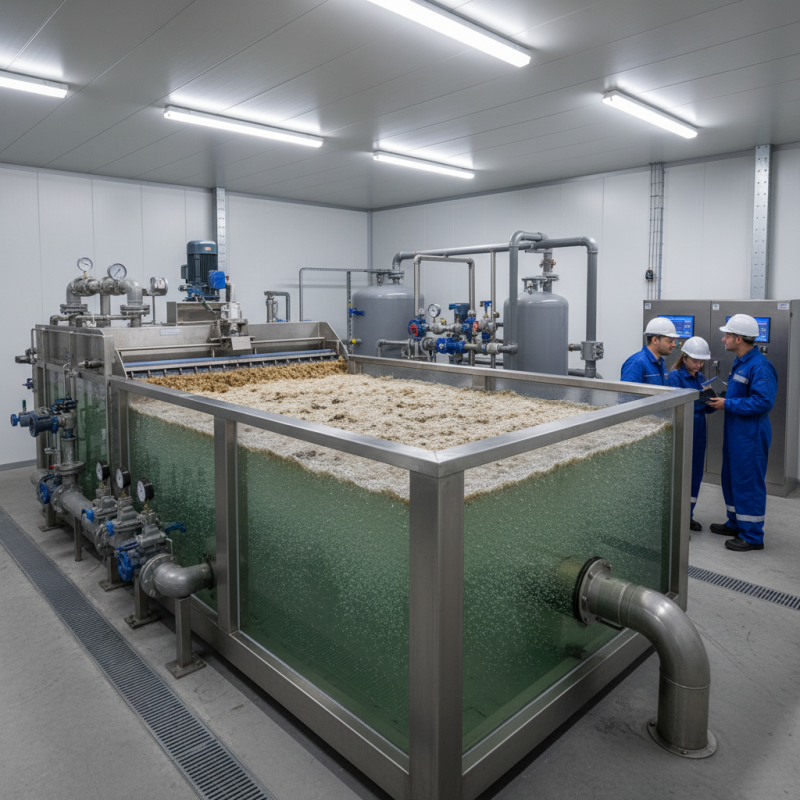

A Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) system efficiently separates suspended solids from liquid waste. This technology is widely used in various industries, including food processing and wastewater treatment. In a typical DAF system, air is dissolved into the influent under pressure. When released, the air forms tiny bubbles that attach to particles, helping them rise to the surface.
DAF systems can remove up to 90% of total suspended solids in some applications. According to a recent industry report, these systems have become increasingly popular due to their effectiveness in treating high-strength wastewater. They are particularly beneficial for handling oily waste. However, startup and operational challenges exist. Not all DAF units achieve the same efficiency. Operator training and system maintenance are critical to their success.
In practice, achieving the ideal air-to-solids ratio is complex. Some facilities report inconsistent performance. Parameters like water temperature and pH levels can influence results. Adequate pre-treatment steps are vital for optimized removal rates. Understanding these factors is key for facilities aiming to enhance their wastewater treatment processes.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) technology is an effective method for wastewater treatment. It relies on the principles of buoyancy and suspended solids separation. In this process, air is dissolved in water under pressure. When released, small bubbles form, attaching to particles and causing them to rise.
The suspended solids float to the surface, forming a scum layer. This layer is then removed, leaving cleaner water. DAF systems are often used in municipal and industrial applications. They are particularly effective for treating oily or greasy wastewater. However, the effectiveness can vary based on the characteristics of the influent.
While DAF technology offers many benefits, it is not without limitations. Sometimes, the bubble size is inconsistent. This can lead to incomplete solids removal. Operators need to monitor the system closely. Regular adjustments may be required to optimize performance. Understanding these principles can help refine the operation of DAF systems, ensuring more efficient treatment.
A Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) system plays a critical role in water treatment. It efficiently removes solids and other impurities through a process where air bubbles attach to particles. But what exactly are the key components that make this system effective?
At the heart of a DAF system, the pressurization unit is vital. It dissolves air into water under pressure. When this pressure is released, micro-bubbles form. These bubbles then adhere to suspended solids, causing them to rise to the surface. This process enhances the removal of up to 90% of suspended solids, a figure highlighted by multiple industry reports.
The separator tank is another essential component. It allows for the collection of floated solids for further processing.
Another important aspect is the chemical dosing unit. It helps in coagulation or flocculation, improving the system’s efficiency. The use of chemicals also raises operational concerns. Overuse can lead to excess sludge, complicating disposal. Monitoring chemical levels becomes crucial.
Lastly, the control panel ensures the entire system functions smoothly. However, it's essential to regularly calibrate this equipment to avoid malfunctions. Overall, maintaining a DAF system requires attention to detail and constant evaluation.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process widely used in various industries. It primarily aims to remove suspended solids, oils, and greases from wastewater. The DAF process consists of several key steps that ensure effective treatment.
Air is dissolved in water under pressure. This pressurized water is mixed with the wastewater. Once the pressure is released, tiny air bubbles form. These bubbles attach to suspended particles, causing them to rise to the surface. The floating sludge is then skimmed off. According to industry studies, DAF systems can remove up to 90% of suspended solids and 95% of fats, oils, and greases when operated correctly.
Tips: Regular maintenance of the DAF unit is essential. Monitor bubble size and flow rates regularly. Inefficiencies can arise from improper air saturation. Also, keep an eye on the sludge blanket thickness. Overloading can lead to ineffective treatment.
Operators sometimes face challenges. The selection of the appropriate chemicals plays a crucial role in the process. Too much or too little can hinder performance. Additionally, fluctuating wastewater characteristics may impact efficiency. Testing is vital to adapt the system properly as water quality changes.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) systems are widely used in various industries. They excel in treating wastewater by removing suspended solids and oils. The process involves creating tiny air bubbles that attach to contaminants. As a result, these bubbles help float the particles to the surface. This efficient separation is crucial for many applications.
In municipal wastewater treatment, DAF systems remove pollutants effectively. They can handle high pollutant loads and improve water clarity. In food and beverage industries, they eliminate oils and grease from processing waste. This ensures compliance with regulations and enhances environmental sustainability. Meanwhile, DAF systems are also applied in industrial settings. They manage effluents from manufacturing processes. However, their operation requires attention. The system’s efficiency can be affected by factors like temperature and chemical balance.
Despite their advantages, DAF systems have limitations. If not maintained correctly, systems can underperform. Regular monitoring is essential for optimal results. Asset managers often overlook maintenance schedules. They may assume it’s a simple fix when things go wrong. Yet, small changes can have a big impact. Ensuring proper operation demands diligence and care. Proper training for staff is also critical to address potential challenges.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| System Type | Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) |
| Operation Principle | Air is dissolved in water under pressure and released at atmospheric pressure in a floatation tank. |
| Applications | Used in wastewater treatment, food processing, and mineral processing. |
| Key Benefits | Effective removal of suspended solids, oils, and grease. |
| Efficiency | Can achieve up to 99% removal efficiency for certain contaminants. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and cleaning; low operating costs. |
| Operational Parameters | Optimized for specific flow rates and chemical dosing. |