In the pursuit of enhanced water treatment efficiency, the significance of Polymer Dosing Control cannot be underestimated. As water treatment facilities face increasing pressures to optimize chemical use and minimize operational costs, implementing a precise Polymer Dosing Control strategy becomes critical. Dr. Emily Harper, a leading expert in water treatment technologies, emphasizes, “Effective polymer dosing not only improves flocculation but also reduces sludge volume, leading to more sustainable water management practices.” This statement underscores the transformative potential of innovative dosing practices on the overall efficacy of treatment processes.
The need for sophisticated Polymer Dosing Control solutions is more pressing than ever, especially in light of stringent environmental regulations and the growing demand for clean water. By carefully adjusting the dosage of polymers, which are essential for coagulation and flocculation, water treatment facilities can achieve better separation of solids from liquids, resulting in clearer effluent and reduced operational burdens. This ultimate guide delves into the intricacies of Polymer Dosing Control, exploring state-of-the-art technologies, best practices, and future trends that will shape the landscape of water treatment for years to come. As we navigate this complex field, the importance of expert insights and empirical data drives the industry towards smarter, more efficient water treatment solutions.

Polymer dosing control plays a pivotal role in enhancing water treatment processes, primarily through its ability to improve flocculation and sedimentation. In water treatment facilities, the careful dosing of polymers helps to aggregate suspended particles, which facilitates their removal during the filtration process. This results in clearer water and more efficient downstream treatment stages. The precise control of polymer dosage not only optimizes water quality but also contributes to cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for chemical additives and minimizing waste generation.
Effective polymer dosing control involves the integration of automated systems that monitor water quality parameters in real time. These systems adjust the amount of polymer added based on specific conditions such as turbidity and flow rates, ensuring a tailored approach to treatment. By employing advanced sensors and control algorithms, operators can achieve consistent results while minimizing the risk of overdosing. This technological enhancement ultimately leads to a more efficient treatment process, reducing operational costs and improving overall performance in water treatment facilities.
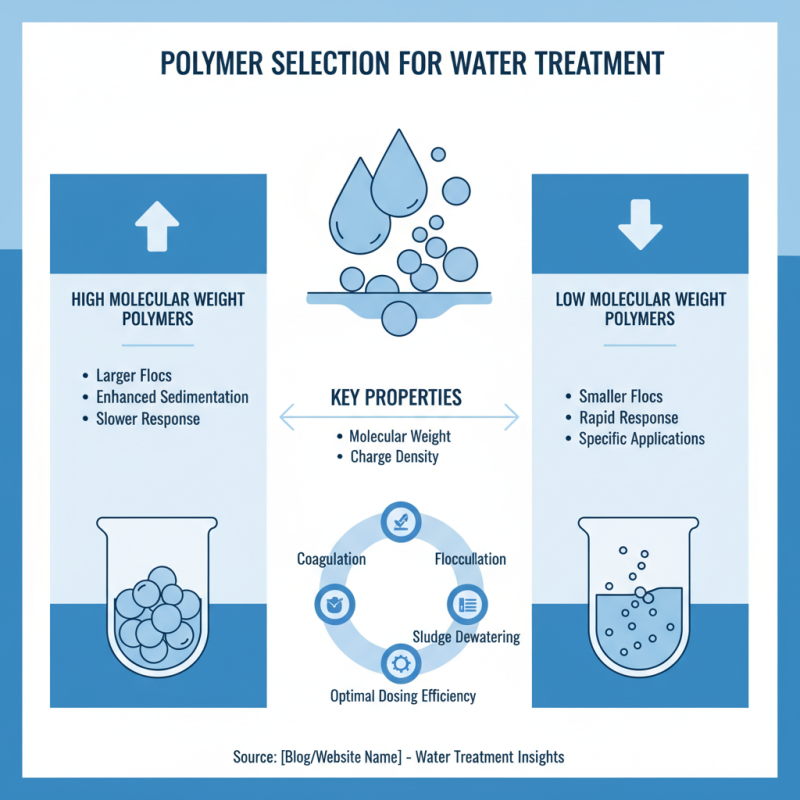
The selection of polymers is a crucial factor for achieving optimal dosing efficiency in water treatment processes. Different types of polymers have unique properties that influence their performance in coagulation, flocculation, and sludge dewatering. For instance, the molecular weight and charge density of a polymer can significantly affect how well it interacts with suspended solids in the water. High molecular weight polymers tend to form larger flocs, enhancing the sedimentation process, while low molecular weight polymers may excel in specific applications requiring a rapid response.
Additionally, the compatibility of the polymer with the water's chemical composition is essential. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of competing ions can alter the effectiveness of the polymer. Conducting thorough water quality assessments prior to polymer selection is vital to ensure that the chosen product aligns with the specific treatment objectives and environmental conditions. By investing time in polymer selection, water treatment facilities can maximize their operational efficiency, reduce costs associated with polymer usage, and ultimately improve the quality of the treated water.
Accurate polymer dosing measurement and control are critical for enhancing the efficiency of water treatment processes. According to a report from the Water Environment Federation, improper dosing can lead to suboptimal flocculation, resulting in increased residuals and longer processing times. One effective technique for achieving accurate polymer dosing is the use of inline monitoring systems equipped with real-time sensors. These systems can measure critical parameters such as flow rates, pressure, and concentration levels of the polymer solution. By continuously adjusting the dosage based on real-time data, operators can ensure that polymers are applied optimally, reducing both chemical costs and environmental impact.
In addition to inline monitoring, advanced control algorithms play a significant role in optimizing polymer dosing. A study published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering highlighted that implementing feedback control systems can improve dosing accuracy by up to 30%. These algorithms analyze system performance and adjust the dosing rates dynamically, taking into account variations in influent water quality and flow conditions. By integrating these techniques into water treatment operations, facilities can enhance their overall treatment efficiency, leading to improved water quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
| Parameter | Value | Units | Measurement Technique |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer Type | Anionic Polyacrylamide | N/A | Manufacturer Specifications |
| Optimal Dosing Rate | 5 | mg/L | Flow Meter Analysis |
| Solution Concentration | 0.1 | g/L | Titration Method |
| Mixing Speed | 300 | RPM | Rotational Viscometer |
| pH Level | 7.5 | pH Units | pH Meter |
| Temperature | 20 | °C | Thermocouple |
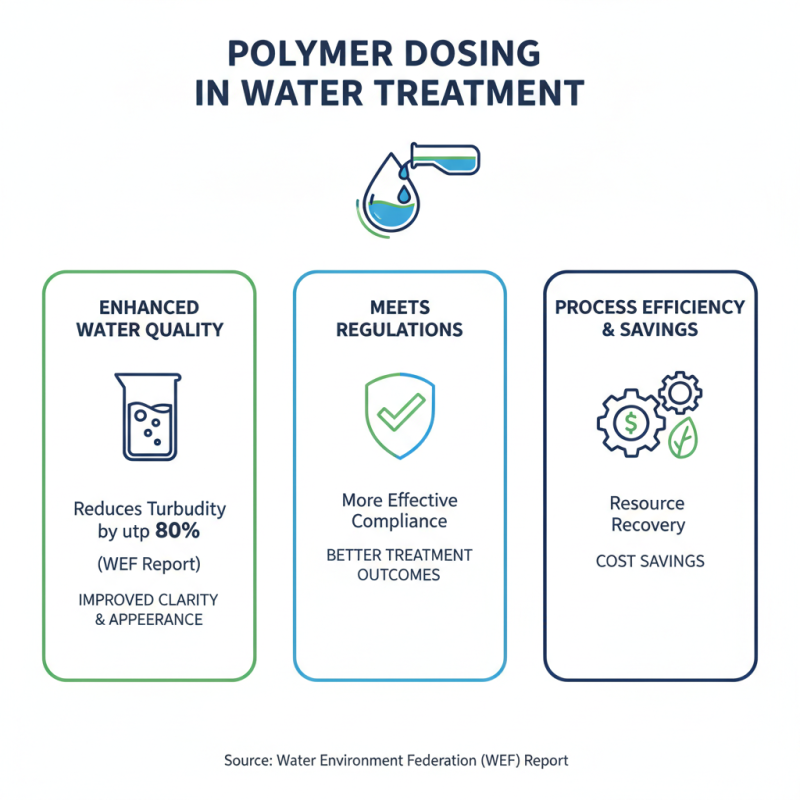
The application of polymer dosing in water treatment processes significantly enhances water quality and treatment outcomes. According to a report by the Water Environment Federation (WEF), proper polymer dosing can reduce turbidity levels by up to 80% in wastewater treatment plants, thereby improving clarity and aesthetics of the treated water. This reduction not only meets regulatory standards more effectively but also has implications for the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment processes, leading to better resource recovery and cost savings.
Moreover, research conducted by the American Water Works Association (AWWA) indicates that optimized polymer dosing can enhance floc formation during coagulation and sedimentation phases, resulting in more efficient removal of suspended solids and organic matter. The data suggests that with optimal dosing controls, facilities can achieve a removal efficiency of 95% or greater for certain pollutants. This level of effectiveness highlights the crucial role that polymers play in not only meeting compliance but also improving the overall performance of water treatment systems. By fine-tuning polymer dosing strategies, operators can adapt to varying influent qualities and ultimately enhance treatment reliability and operational efficiency.
Monitoring and adjusting polymer dosing in real-time operations is crucial for optimizing water treatment processes. The effectiveness of polymer flocculants heavily relies on accurate dosing, which directly impacts the overall efficiency of the purification process. By implementing advanced monitoring systems, operators can measure real-time data on parameters such as flow rates, turbidity, and the chemical composition of wastewater. This enables a responsive approach to dosing adjustments, ensuring that the amount of polymer used is fine-tuned to the specific conditions of the water being treated.
Real-time adjustments not only enhance the efficiency of polymer usage but also contribute to significant cost savings. By continuously analyzing operational parameters, systems can identify fluctuations in water quality that necessitate immediate changes in dosage. This proactive management minimizes the risks of under-dosing or over-dosing, both of which can lead to ineffective treatment and increased operational costs. Furthermore, leveraging automation and advanced control algorithms can streamline the dosing process, allowing for quicker responses to changing conditions while maintaining consistent treatment outcomes. Ultimately, these strategies create a more resilient water treatment system capable of adapting to varying challenges effectively.
This chart illustrates the relationship between polymer dosing amounts and turbidity levels in water treatment operations over a week. The data highlights how real-time adjustments in polymer dosing can optimize treatment efficiency.






